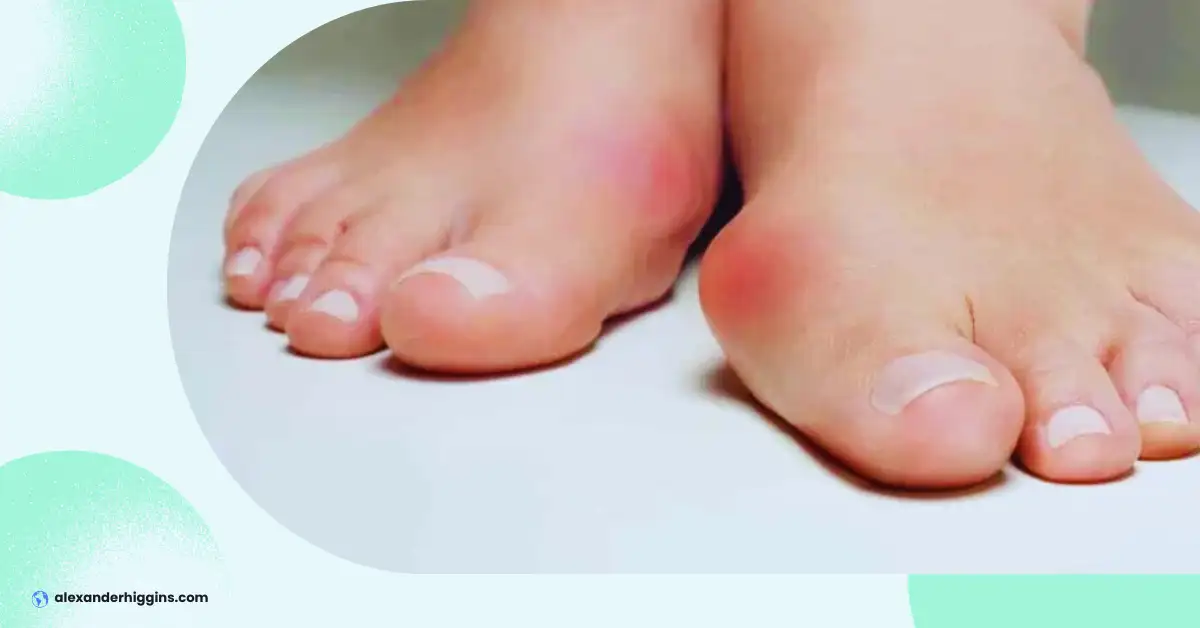
Are you dealing with persistent foot discomfort that’s disrupting your daily routine? Seeking timely diagnosis and treatment from the right healthcare provider is crucial. The sooner you address it, the sooner you can get back to pain-free mobility and enjoy your usual activities. Dive into our discussion on plantar plate injuries to understand what you need to know.
Underneath the toes, there’s a prominent bump known as the ball of the foot. Within this bump lie disc-shaped fibrous ligaments called plantar plates, each corresponding to one of the ten toes. These plates play a vital role in shielding both the toes and the metatarsals (the bones located just beneath the toes) from excessive pressure, especially during strenuous activities like running.
What Are Plantar Plate Injuries?

Plantar plate injuries are a type of foot injury that affects the plantar plate, which is a thick ligament under the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints of the foot. These injuries often occur at the second MTP joint and can cause pain, swelling, and instability in the toe joint.
Plantar plate injuries are common in athletes and dancers who put repetitive stress on the balls of their feet. They can range from plantar plate sprains and tears to complete ruptures of the ligament. Proper diagnosis often involves imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound. Treatment depends on the severity but may involve immobilization, orthotics, injections, or in some cases, surgery to repair the torn ligament.
What causes a plantar plate to tear?
The plantar plate is a thick ligament located under the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints of the foot, particularly the second MTP joint. This ligament plays a crucial role in stabilizing the toe joints and allowing for proper weight transfer while walking and running. A plantar plate tear can occur due to several factors:
1. Acute Trauma: A sudden forceful injury, such as a stubbed toe or a direct impact on the ball of the foot, can cause the plantar plate to tear or rupture.
2. Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repetitive pressure or stress on the ball of the foot, such as ballet dancing, running, or sports involving jumping and pivoting, can lead to gradual weakening and eventual tearing of the plantar plate over time.
3. Abnormal Foot Mechanics: Certain foot deformities or structural problems, such as bunions, hammertoes, or flatfeet, can alter the distribution of forces on the foot and increase the strain on the plantar plate, predisposing it to injury.
4. Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too tight or have inadequate support can increase the risk of developing a plantar plate tear.
Signs and symptoms of plantar plate injuries
Plantar plate injuries can cause various symptoms that may indicate an issue with this important ligament structure under the balls of the feet. Some of the common signs and symptoms of plantar plate injuries include:
Diagnosing a plantar plate injury typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional. Signs that may indicate a plantar plate tear include:
- Pain: One of the most noticeable signs is localized pain and tenderness directly on the ball of the foot, particularly under the second toe joint. The pain often worsens with weight-bearing activities or when bending the toe up or down.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the affected toe joint are common signs of a plantar plate injury. The swelling may be visible and can also cause a “fat toe” appearance.
- Instability: As the plantar plate ligament weakens or tears, it can lead to instability and abnormal movement of the toe joint. The toe may appear to shift or drift out of alignment.
- Bruising: In some cases, particularly with acute tears or ruptures, bruising may appear on the ball of the foot or around the affected toe joint.
- Difficulty Walking: Plantar plate injuries can make it painful and difficult to walk normally, especially with activities that involve pushing off from the balls of the feet.
- Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch, particularly when pressure is applied to the ball of the foot.
- Laxity: In more severe cases, there may be noticeable laxity or looseness in the affected toe joint, indicating a significant tear in the plantar plate.
- Limited range of motion: A plantar plate tear can restrict the normal range of motion of the affected toe, leading to stiffness and difficulty with movement.
Prevention of plantar plate injuries
Preventing plantar plate injuries is essential, especially for individuals involved in activities that place repetitive stress on the balls of the feet, such as dancers, runners, and athletes. By taking proactive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing this painful condition and avoid potential complications. Some key strategies for plantar plate injury prevention include:
1. Ice therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling, particularly after activity or injury.
2. Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and providing adequate rest can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
3. Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes with adequate cushioning and support, particularly in the forefoot area, can help distribute forces more evenly and minimize excessive stress on the plantar plate.
4. Foot Strengthening Exercises: Incorporating exercises that strengthen the intrinsic muscles of the feet and improve flexibility can help maintain proper foot mechanics and reduce strain on the plantar plate.
5. Gradual Progression: If you’re starting a new activity or increasing the intensity of your training, it’s important to progress gradually to allow your body, including your feet, to adapt to the increased demands.
6. Biomechanical Assessment: Consulting with a podiatrist or physical therapist can help identify any underlying biomechanical issues, such as overpronation or high arches, which may predispose you to plantar plate injuries. Appropriate orthotics or other corrective measures can be recommended.
7. Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Adequately warming up before physical activity and cooling down afterward can help prepare the muscles and tissues for the demands of the activity and aid in recovery.
Treatment for a plantar plate injury
Treatment for a plantar plate injury depends on the severity of the tear and the individual’s symptoms. In mild cases, conservative measures may be sufficient to relieve pain and promote healing. These may include:
1. Orthotic devices: Custom orthotic inserts or padding may be recommended to provide support and reduce pressure on the affected area.
2. Immobilization: For acute or severe plantar plate tears, immobilizing the affected foot in a walking boot, cast, or splint is often recommended initially to restrict motion and protect the area as it heals.
3. Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain and swelling associated with plantar plate injuries.
4. Orthotic Devices: Using stiff-soled shoes, metatarsal pads, or custom orthotics can help offload pressure from the injured plantar plate and provide support during the healing process.
5. Physical Therapy: Once the initial pain and swelling have subsided, physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the foot muscles, improve flexibility, and retrain proper foot mechanics.
6. Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, particularly in chronic or refractory cases.
7. Surgery: For plantar plate tears or ruptures that fail to respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged ligament.
In more severe cases or if conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the torn plantar plate and restore stability to the affected toe.
Also read: How To Cure Plantar Fasciitis In One Week: Fast-Track Healing Methods!
Conclusion
A plantar plate tear can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and return to their normal activities. Understanding plantar plate injuries is vital for anyone experiencing persistent foot discomfort.
From recognizing symptoms to exploring preventive measures and treatment options, this overview emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis and intervention. By prioritizing proper foot care, individuals can minimize the impact of plantar plate injuries, regain pain-free mobility, and continue enjoying their daily activities with confidence and comfort.
Frequently asked questions
A: Plantar plate tears can be caused by various factors, including bunions, over-pronation (rolling the feet inward), hammertoes, and engaging in high-pressure activities such as running, dancing, or climbing stairs. These conditions and activities can exert excessive strain on the plantar plate, leading to its weakening and eventual tearing.
A: Yes, bunions are recognized as one of the contributors to plantar plate tears. The misalignment of the big toe joint associated with bunions can increase pressure on the plantar plate, potentially causing its thinning, stretching, and eventual tearing.
A: Plantar plate tears can occur due to a combination of factors such as over-pronation, the presence of bunions, hammertoes, and participating in activities that place significant pressure on the balls of the feet. These factors can gradually weaken the plantar plate, making it more susceptible to tearing.
A: Recovery from a plantar plate tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury and individual factors. However, the majority of patients report being pain-free within 3-4 months after receiving appropriate treatment aimed at restoring the integrity of the plantar plate.
A: Depending on the severity of the tear, your doctor may advise you to refrain from walking barefoot to prevent aggravating the injury further. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s guidance regarding activity modification and treatment to facilitate proper healing.
Reference
- Nery C, Raduan FC, Catena F, Mann TS, de Andrade MA, Baumfeld D. Plantar plate radiofrequency and Weil osteotomy for subtle metatarsophalangeal joint instability. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:180.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4653840/