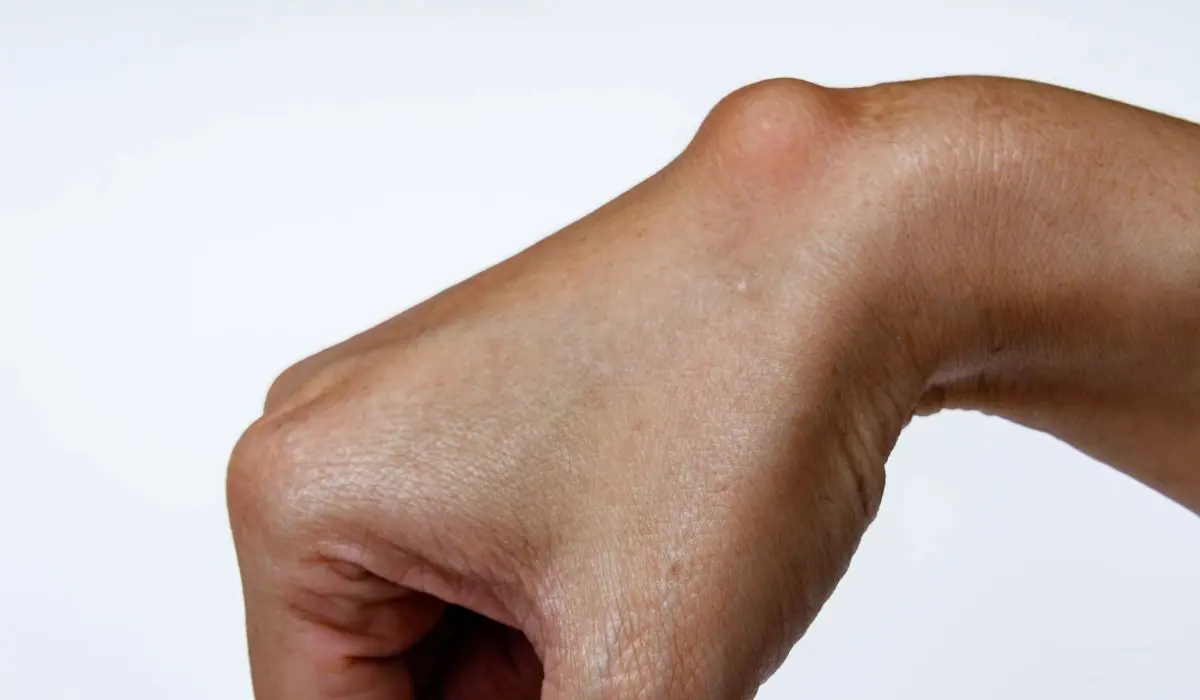
Have you ever noticed a mysterious lump on your wrist, hand, ankle, or foot? Chances are, it could be a ganglion cyst – a non-cancerous, fluid-filled swelling that often arises near joints or tendons. While these cysts are generally harmless, their appearance can be concerning, leaving many individuals wondering about their underlying causes.
Interestingly, recent research has sparked discussions about a potential link between ganglion cysts vitamin deficiency, particularly vitamin D deficiency.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of ganglion cysts, explore the causes of vitamin deficiencies, and investigate the fascinating relationship between these two seemingly unrelated conditions.
Ganglion Cyst: An Overview
Ganglion cysts are small, benign lumps that typically form near joints or tendons, most commonly on the wrist, hand, ankle, or foot. These cysts are filled with a viscous, jelly-like fluid and can range in size from a pea to a golf ball.
While they may appear alarming, ganglion cysts are generally harmless and often go away on their own without treatment.
However, in some cases, these cysts can cause discomfort, pain, or numbness, especially if they press on nearby nerves or restrict joint movement.
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains uncertain, but they are believed to arise from injuries, repetitive stress, or joint or tendon irritation.
What Causes Vitamin Deficiency?
Vitamin deficiencies occur when the body doesn’t receive sufficient amounts of essential vitamins from the diet or through other means, such as sunlight exposure or supplements. Various factors can contribute to vitamin deficiencies, including:
1. Inadequate Dietary Intake
A diet lacking in nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can lead to vitamin deficiencies.
2. Malabsorption Issues
Certain medical conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or gastric bypass surgery, can impair the body’s ability to absorb vitamins from food.
3. Strict Dietary Restrictions
Individuals following strict vegetarian or vegan diets may be at risk of developing deficiencies in certain vitamins, such as vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Lack of sun exposure, which is essential for vitamin D production, or excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to vitamin deficiencies.
5. Medications And Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as antibiotics or weight-loss drugs, can interfere with vitamin absorption or metabolism, while chronic illnesses like kidney or liver disease can also lead to vitamin deficiencies.
Ganglion Cyst Vitamin Deficiency: Link Between Them
While the direct connection between ganglion cysts and vitamin deficiency has not been conclusively established, emerging research suggests that there may be an intriguing relationship between the two. One of the primary vitamins of interest is vitamin D, which plays a crucial role in bone health, immune function, and nerve growth.
Several studies have explored the potential impact of vitamin D deficiency on nerve health and the development of certain conditions related to nerve function. For instance, one study conducted on rats found that vitamin D deficiency led to a loss of nerve connections in the synovium, the thin membrane lining the joints.
Another study observed an association between vitamin D deficiency and thinning of the retinal ganglion cell complex, an integral part of the nervous system, in older adults.
While these findings do not directly link ganglion cysts to vitamin deficiency, they highlight the potential influence of vitamin D on nerve health and function, which could have implications for the development of ganglion cysts.
Since these cysts often form near joints and tendons, where nerve endings are present, it is possible that vitamin D deficiency could contribute to nerve irritation or dysfunction, potentially increasing the risk of cyst formation.
However, it is important to note that the relationship between ganglion cysts and vitamin deficiency is still a subject of ongoing research, and more studies are needed to establish a definitive causal link.
Other factors, such as injury, repetitive stress, and joint or tendon irritation, are also known to play a role in the development of ganglion cysts.
Conclusion
While the connection between ganglion cyst vitamin deficiency remains an area of scientific exploration, maintaining adequate vitamin levels, particularly vitamin D, is crucial for overall health and well-being.
If you suspect a vitamin deficiency or have concerns about a ganglion cyst, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
By adopting a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods, ensuring sufficient sun exposure (or taking supplements if necessary), and addressing any underlying medical conditions, you can help prevent vitamin deficiencies and potentially reduce the risk of developing ganglion cysts or other related health issues.
Remember, the human body is a complex system, and various factors can contribute to the development of conditions like ganglion cysts.
By embracing a holistic approach that combines proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and proactive healthcare, you can promote overall well-being and potentially mitigate the impact of ganglion cyst vitamin deficiency or other health concerns.
References
- WebMD (2005-2024) What Is a Ganglion Cyst? Available Online at: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/ganglion-cyst
- NIH (n.d) Main nutritional deficiencies Available Online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9710417/